As we age, our bodies naturally undergo changes, and maintaining good health becomes a top priority. One of the most effective ways to promote longevity and ensure that we enjoy a long, healthy life is through consistent exercise. Physical activity has been shown to improve various aspects of our health, from cardiovascular fitness to mental well-being, and it plays a key role in preventing chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and even cancer. By incorporating the right types of exercise into our daily routines, we can not only extend our lifespan but also enhance our quality of life as we age.
The connection between exercise and longevity is undeniable, and research consistently points to the fact that staying active is one of the most important factors in aging well. However, not all forms of exercise are created equal. Some workouts are better suited for promoting long-term health and longevity, providing benefits that keep us strong, mobile, and energized well into our later years. In this post, we will explore the best workouts that can help you maintain your health and vitality throughout your life, ensuring that you stay active and capable no matter your age.
Cardiovascular Exercise: The Heart of Longevity
Cardiovascular exercise, often referred to as aerobic exercise, is any activity that raises your heart rate and keeps it elevated for an extended period. Walking, running, cycling, swimming, and dancing are all examples of cardiovascular exercises that are essential for maintaining good health as we age. These activities help strengthen the heart, improve lung capacity, and increase blood circulation, all of which contribute to overall longevity.
One of the primary benefits of cardiovascular exercise is its ability to reduce the risk of heart disease, the leading cause of death worldwide. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, and lowers blood pressure, helping to maintain a healthy cardiovascular system. It also plays a crucial role in managing weight, improving cholesterol levels, and reducing the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular issues.
In addition to its physical benefits, cardiovascular exercise has been linked to improved brain health. It increases the flow of oxygen to the brain, promotes the growth of new brain cells, and enhances cognitive function. Studies have shown that people who engage in regular aerobic exercise are less likely to experience cognitive decline and are at a lower risk for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
Incorporating at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise each week—such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming—can go a long way in promoting longevity. For those looking for a more vigorous workout, activities like running, hiking, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can also provide significant benefits for heart health and overall well-being.
Strength Training: Building Muscle for a Stronger Future
As we age, we naturally lose muscle mass, a process known as sarcopenia. This loss of muscle can lead to weakness, frailty, and a higher risk of falls and fractures. Strength training, or resistance exercise, is an effective way to combat muscle loss and preserve strength and function as we get older. By using weights, resistance bands, or even body weight exercises, strength training helps build muscle, improve bone density, and increase metabolism, all of which contribute to better long-term health.
One of the key benefits of strength training is its ability to maintain and even increase muscle mass as we age. Regular resistance exercise stimulates muscle growth and helps prevent the natural decline in muscle tissue that occurs with aging. Strong muscles are essential for maintaining balance and stability, which reduces the risk of falls and injuries. Additionally, strength training helps improve joint health by increasing flexibility and range of motion, which is crucial for staying active and independent as we age.
Strength training also plays an important role in maintaining bone health. Weight-bearing exercises stimulate the production of bone-forming cells and help prevent osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones that are more susceptible to fractures. Studies have shown that people who engage in regular strength training have stronger bones and are less likely to experience fractures and other bone-related issues.
For optimal results, aim to incorporate strength training into your routine at least two to three times a week. Focus on exercises that target all major muscle groups, including the legs, back, chest, arms, and core. Whether using free weights, machines, or bodyweight exercises like squats and push-ups, strength training is a crucial component of a well-rounded fitness routine that supports long-term health.
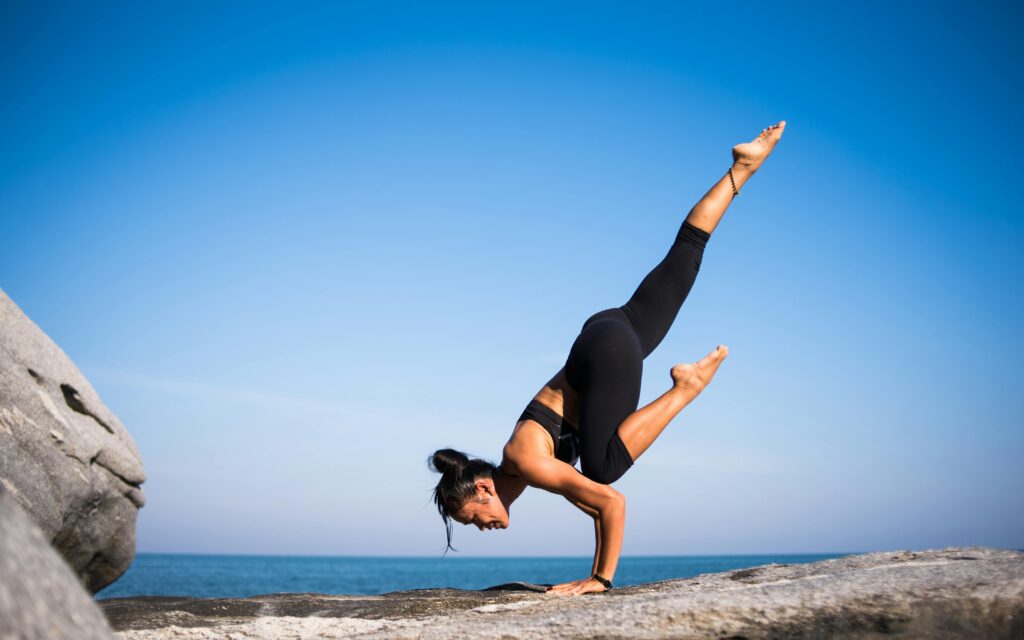

Flexibility and Mobility: Keeping Your Body Agile
As we age, our muscles and joints naturally lose some of their flexibility and range of motion. This can lead to stiffness, discomfort, and a reduced ability to perform everyday tasks. Stretching exercises, yoga, and Pilates are all excellent ways to maintain flexibility and mobility, which are key factors in ensuring that we remain active and independent throughout our lives.
Stretching helps to lengthen the muscles and improve flexibility, which in turn enhances joint function and reduces the risk of injuries. Regular stretching can alleviate muscle tension, improve posture, and increase circulation, all of which contribute to better overall health. It also helps to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve mental clarity, making it a great addition to any wellness routine.
Yoga and Pilates, both of which incorporate stretching, breathing, and mindfulness, are especially beneficial for promoting flexibility and mobility. These practices emphasize body alignment, balance, and coordination, which help improve posture, reduce the risk of falls, and enhance overall body awareness. Additionally, yoga and Pilates are low-impact exercises, making them suitable for people of all ages and fitness levels.
Incorporating flexibility and mobility exercises into your routine can help prevent injuries, ease chronic pain, and improve your ability to perform everyday tasks like bending, reaching, and walking. Consider setting aside time each day for stretching or participating in a yoga or Pilates class a few times a week to keep your body agile and functional.
Balance and Coordination: Preventing Falls and Improving Stability
As we age, maintaining balance and coordination becomes increasingly important. Falls are a leading cause of injury and disability among older adults, and improving balance can significantly reduce the risk of falls. Activities that challenge your balance, such as tai chi, balance exercises, or even simple standing on one leg, can help improve stability and prevent falls.
Tai chi, a traditional Chinese martial art that emphasizes slow, controlled movements and deep breathing, has been shown to improve balance, strength, and flexibility. It is particularly beneficial for older adults, as it can be practiced at a gentle pace and adapted to individual fitness levels. Research has shown that regular tai chi practice can help reduce the risk of falls, improve posture, and enhance overall mobility.
Other balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or practicing balance on a stability ball, can also help improve coordination and stability. These exercises challenge the body’s ability to maintain balance while engaging the core muscles and promoting better posture.
Incorporating balance and coordination exercises into your routine a few times a week can help improve stability, reduce the risk of falls, and ensure that you remain active and independent as you age.
Mental Health and Mindfulness: The Role of Exercise in Emotional Well-Being
While physical exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy body, it also plays a crucial role in supporting mental and emotional well-being. Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress, and it promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Additionally, exercise helps improve sleep quality, boost energy levels, and increase self-esteem, all of which contribute to a positive mental state.
Incorporating mindfulness practices into your exercise routine, such as focusing on your breath during yoga or practicing deep breathing during walking or running, can further enhance the mental health benefits of physical activity. Mindfulness-based exercises help to reduce stress, increase relaxation, and improve overall mental clarity.
Exercise not only strengthens the body but also supports emotional resilience, making it an essential component of any longevity-focused fitness routine.
Conclusion
Exercise is one of the most powerful tools we have for promoting longevity and ensuring that we live healthy, active lives well into our later years. By incorporating cardiovascular exercise, strength training, flexibility and mobility exercises, balance and coordination training, and mindfulness into your routine, you can support both your physical and mental health, ensuring that you stay strong, agile, and capable as you age.
It’s important to remember that the key to longevity is consistency. Whether you’re just starting your fitness journey or have been active for years, it’s never too late to make exercise a priority in your life. By making exercise a regular part of your routine, you can unlock the benefits of better health, increased vitality, and a higher quality of life—helping you enjoy a long, happy, and healthy future.